
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Establish Clear Farming Goals
- Conduct Soil Testing and Fertility Enhancement
- Select Suitable Crops and Livestock
- Plan Your Farming Calendar
- Adopt Climate-Smart Agriculture
- Secure Market Access and Funding
- Utilize Mechanization and Agri-Tech Solutions
- Conclusion
- References
- Contact HTSF Global
Introduction
Agriculture remains a backbone of the Nigerian economy, providing employment, food security, and raw materials for various industries. The sector contributes significantly to the country’s GDP and supports the livelihoods of millions, from smallholder farmers to large-scale agribusinesses. However, despite its importance, many farmers face persistent challenges such as poor planning, low yields, erratic weather conditions, pest infestations, and limited access to modern farming tools.
With rapid changes in climate patterns, fluctuating market demands, and the growing need for sustainable farming practices, proper seasonal planning has become essential for ensuring both short-term success and long-term resilience in the agricultural sector. As a farmer, you must proactively plan your farming activities to optimize resources, improve crop and livestock productivity, and minimize losses due to unforeseen circumstances.
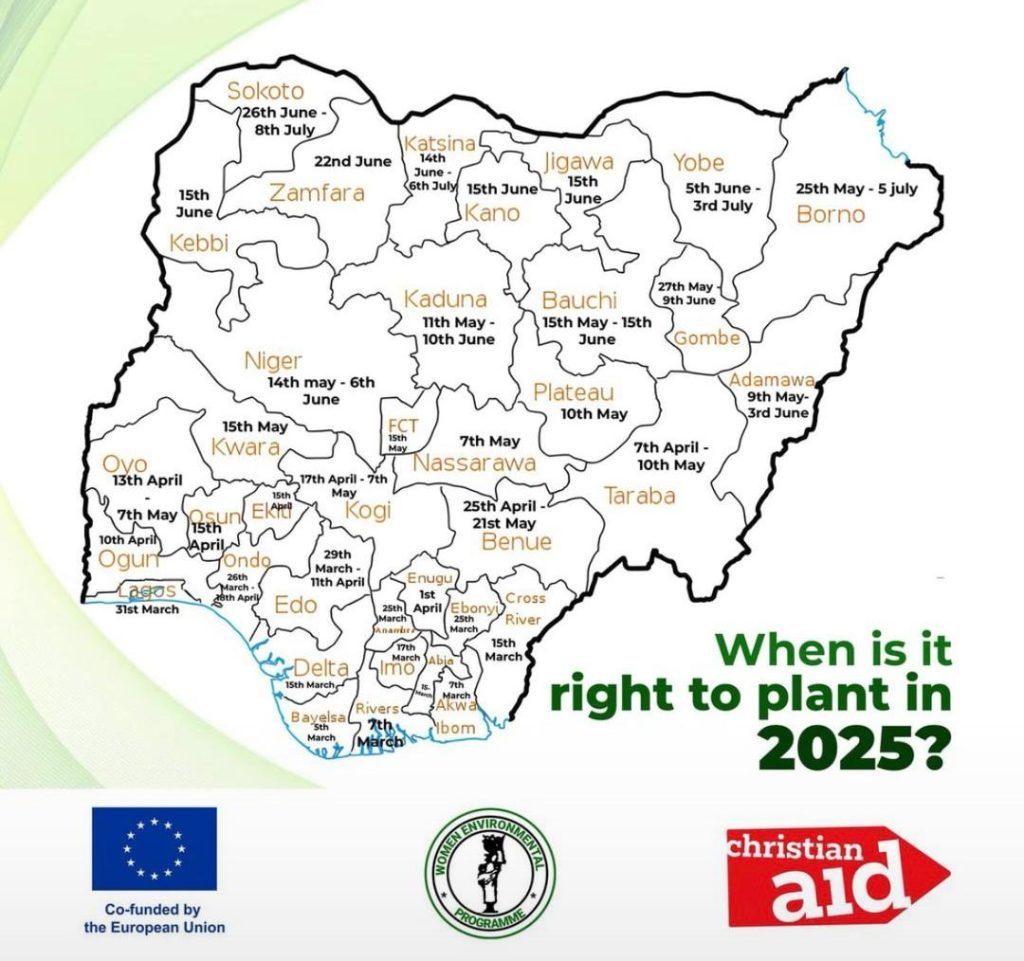
This article provides practical, expert-backed strategies from HTSF Global, covering key aspects such as soil health, climate-smart agriculture, mechanization, and financial planning. By implementing these strategies, you can enhance your productivity, maximize profitability, and contribute to food security in Nigeria and beyond.
1. Establish Clear Farming Goals
Before the planting season begins, farmers should set realistic, specific, and measurable goals to guide their activities and maximize efficiency. These goals should be tailored to their available resources, environmental conditions, and market demand. Some key objectives farmers can consider include:
- Increasing yield per hectare by adopting improved seed varieties, precision farming techniques, and better soil management practices.
- Expanding farm size through proper land acquisition, mechanization, and efficient land use planning.
- Enhancing soil fertility by integrating organic and inorganic soil amendments, practicing crop rotation, and employing conservation agriculture methods.
- Adopting climate-smart agriculture to mitigate the effects of climate change, such as drought-resistant crop selection, water conservation techniques, and integrated pest management.
In addition to setting agricultural goals, farmers should develop a comprehensive financial plan that includes cost estimation and revenue projection. This plan should cover key expenses such as seed procurement, fertilizers, irrigation systems, labor costs, and equipment maintenance. Farmers should also explore potential funding sources, such as agricultural grants, microloans, and government subsidies, to ease financial constraints.
By establishing well-defined goals and a structured financial roadmap, farmers can monitor their progress throughout the season, make informed decisions, and swiftly adapt to any challenges that arise, ultimately leading to a more productive and profitable farming operation.
2. Conduct Soil Testing and Fertility Enhancement
Soil health is one of the most critical factors influencing crop productivity and overall farm success. As a farmer, you should conduct comprehensive soil testing before planting to determine essential parameters such as nutrient levels, organic matter content, pH balance, and microbial activity. Soil testing can be performed through agricultural extension services, private laboratories, or DIY soil test kits.
Understanding your soil composition enables you to apply targeted solutions that enhance soil fertility and structure. Based on the test results, the following soil improvement methods can be implemented:
In addition to addressing specific deficiencies, farmers should integrate long-term soil fertility management strategies, including:
- Crop rotation to prevent nutrient depletion and disrupt pest cycles.
- Cover cropping (e.g., legumes, clover) to improve soil structure, nitrogen fixation, and moisture retention.
- Organic fertilization using compost, farmyard manure, and biofertilizers to enrich microbial activity and maintain soil biodiversity.
- Minimal tillage practices to prevent erosion and enhance soil carbon sequestration.
As a farmer, you should avoid excessive reliance on chemical fertilizers, as improper application can lead to soil degradation, water pollution, and loss of beneficial microorganisms. Instead, a balanced approach incorporating organic amendments and precision nutrient application should be adopted for sustainable soil health and long-term productivity.
3. Select Suitable Crops and Livestock
Choosing the right crops and livestock depends on climate, soil type, and market demand. Farmers should consider:
- Drought-resistant crops (e.g., maize, sorghum) in arid regions
- Leguminous crops (e.g., cowpea, soybeans) for nitrogen fixation
- Hybrid seeds for higher yields and disease resistance
For livestock farming, farmers should ensure adequate feeding, vaccination, and housing to reduce losses. Access to veterinary services is also crucial for maintaining livestock health. Proper management practices, such as rotational grazing and improved breeding techniques, can enhance productivity.
4. Plan Your Farming Calendar
A structured farming schedule is essential for timely planting and harvesting. As a farmer, you should align your activities with seasonal weather patterns and regional agricultural guidelines to optimize yield and efficiency. Proper planning allows you to prepare for input purchases, labor management, and pest control measures in advance.
Key Factors to Consider When Planning Your Calendar
- Climate Conditions: Analyze historical weather data and use forecasting tools to predict rainfall patterns.
- Soil Preparation Timing: Start land preparation early to ensure the soil is in optimal condition before planting.
- Seed Selection & Procurement: Source high-quality seeds from trusted suppliers before the planting window closes.
- Crop Rotation Planning: Organize which crops to plant to prevent soil nutrient depletion.
- Pest and Disease Control Schedule: Set up a plan for early intervention and monitoring of potential threats.
To further refine your calendar, you should integrate weather forecasting tools, mobile apps, and extension services that provide real-time guidance on optimal planting dates, fertilizer application timing, and pest outbreaks. A well-planned farming calendar ensures that you avoid losses due to late planting or adverse weather conditions.
5. Adopt Climate-Smart Agriculture
With increasing climate unpredictability, it is essential for farmers to incorporate climate-smart practices into their operations. Climate-smart agriculture ensures that you use resources efficiently while maintaining soil fertility and protecting the environment. Below are some key climate-smart agricultural practices you should adopt:
Water Conservation Strategies
Efficient water management is critical for successful farming. As a farmer, you should implement strategies that optimize water usage, especially during dry seasons. Drip irrigation is a proven technique that delivers water directly to plant roots, minimizing wastage. Rainwater harvesting is another essential method, allowing you to collect and store rainwater for use during periods of drought. Additionally, mulching with organic materials such as straw or dried leaves helps retain soil moisture, regulate temperature, and reduce water stress on crops.
Soil and Land Management
Maintaining soil health is fundamental to achieving high yields. You should consider agroforestry, which involves planting trees and shrubs on your farmland to reduce erosion, improve soil fertility, and increase carbon sequestration. Cover cropping with legumes like cowpeas and groundnuts improves soil structure and enhances water retention, reducing the risk of soil degradation. Additionally, minimum tillage is an effective technique that limits soil disturbance, preserves microbial activity, and prevents erosion.
Integrated Pest and Disease Management
Managing pests and diseases effectively without harming the environment requires an integrated approach. Instead of relying solely on chemical pesticides, you should consider biological control methods, such as introducing natural predators like ladybugs to manage pests. Crop diversification is another important strategy by planting multiple crops, you reduce the risk of a disease outbreak devastating your entire farm. Additionally, selecting resistant crop varieties helps prevent common pest infestations and diseases, ensuring a more resilient farm.
Sustainable Livestock Farming
If you are involved in livestock farming, sustainable practices can help you maintain productivity while minimizing environmental impact. Rotational grazing is a technique where you move livestock between different pastures, allowing forage to regenerate and preventing overgrazing. Feed optimization ensures that your animals receive high-quality, locally available feed to improve productivity and reduce costs. Furthermore, you can engage in waste recycling by converting livestock waste into organic manure or biogas, reducing environmental pollution and improving farm sustainability.
6. Secure Market Access and Funding
As a farmer, you must explore market opportunities before harvesting. Strategies for securing buyers include:
- Partnering with agricultural cooperatives
- Leveraging HTSFarms e-commerce platform (embed farms link)
- Establishing supply agreements with food processors
For funding, you can access government grants, microfinance loans, and private investments to expand operations. Crowdfunding and digital finance platforms also provide new opportunities for raising capital.
7. Utilize Mechanization and Agri-Tech Solutions
Modern farming requires mechanization to improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, and increase productivity. As a farmer, you should take advantage of technology-driven solutions such as:
- Tractors, tillers, and mechanized harvesters to reduce manual labor and enhance efficiency.
- Drones and satellite imaging for monitoring crop health and detecting pest infestations early.
- Mobile applications and USSD services for market access, weather updates, and financial transactions.
HTSFarms partners with Zoomlion to provide affordable mechanization solutions to farmers. Additionally, farmers should explore digital tools for supply chain management and financial transactions to streamline their operations.
Conclusion
A well-planned farming season enhances productivity, profitability, and sustainability. As a farmer, you should adopt strategic planning, soil management, climate-smart agriculture, mechanization, and modern technology to maximize your yield and revenue. Investing in these best practices not only secures your farm’s success but also contributes to food security and economic growth.
HTSF Global remains committed to empowering farmers with innovative solutions, training programs, and access to premium agricultural inputs. By leveraging expert advice and adopting modern techniques, you can position yourself for a successful farming season and long-term agricultural prosperity.
References
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). (2023). Sustainable Agriculture and Food Security in Africa. FAO Publications.
International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA). (2022). Best Practices for Smallholder Farmers in Nigeria. IITA Research Paper.
Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development (2024). National Agricultural Policy Guidelines. Federal Government of Nigeria.
